Trending...
- DanReDev, Kaufman Development & Oldivai Announce Major 2026 Projects Nationwide
- "I Make Music Not Excuses" Journal by Anthony Clint Jr. Becomes International Amazon Best Seller, Empowering Music Creators Worldwide
- Consortium Media Appoints Jennifer Curtis-Neves as President of Consortium Media
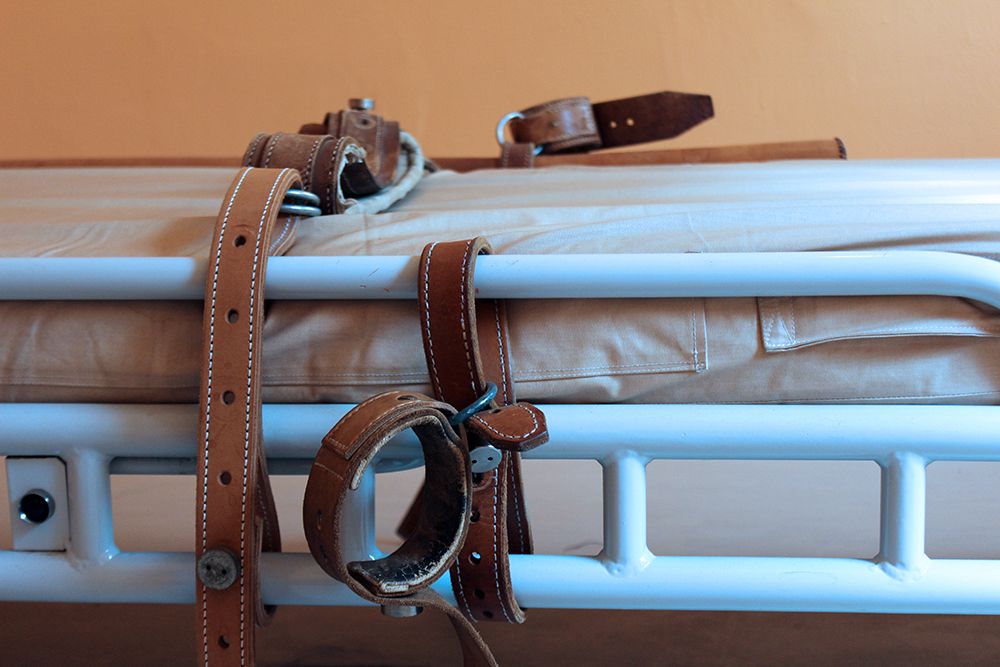
As the nation observes Black History Month, the Citizens Commission on Human Rights highlights racial disparities in restraint-related deaths and advocates for legislative change to protect vulnerable patients.
LOS ANGELES - Californer -- The Citizens Commission on Human Rights (CCHR) International commends the introduction of a new bill in Hawaii that prohibits the use of life-threatening restraints and seclusion in psychiatric hospitals, particularly for minors and vulnerable adults. This bill, introduced by Representative Elijah Pierick, sets a vital precedent for other U.S. states to follow, aiming to protect patients from traumatic and often lethal restraint practices.[1]
CCHR underscores the importance of this legislation during Black History Month, spotlighting the alarming over-representation of racial minorities among those subjected to restraints and seclusion in the mental health system. The bill only permits the use of restraint in rare instances where there is an immediate risk of harm to the patient or others, and only after less intrusive measures have been attempted.
A 2011 report found that African Americans were disproportionately affected by restraint-related deaths, making up 22% of the studied deaths while only comprising 13% of the U.S. population. In addition, Black and multiracial patients are more likely to experience restraints, often for longer periods, than their white peers.[2] In 2021, a study of adults receiving an emergency psychiatric evaluation between January 1, 2014, and September 18, 2020, at a large academic medical center revealed Black patients continued to be at higher risk of experiencing physical or chemical restraint compared with White patients.[3]
Responding to high numbers of restraint deaths, in 2020, CCHR formed its Task Force Against Racism and Modern-Day Eugenics, led by Reverend Frederick Shaw, aimed at ending physical and chemical restraint deaths, particularly prevalent among minority communities.
More on The Californer
This followed the death of a 16-year-old African American boy after being restrained in the now-closed residential behavioral facility for teens in Michigan. The Kalamazoo County Medical Examiner's office determined the death was a homicide and three staff were charged with involuntary manslaughter and second-degree child abuse—all pleading guilty.[4]
Two years later, another shocking tragedy was the death of a 7-year-old foster care child who was restrained and killed at a psychiatric residential center in Louisville, Kentucky on July 17, 2022. In September, the medical examiner also ruled that death a homicide.[5]
Their deaths underscored the urgent need for legislative action because, despite the clear risks, the practice of using seclusion and mechanical restraints remains common in psychiatric facilities. A 2023 report from Psychiatric Services issued a call for regulatory action to end these practices due to the significant trauma and potential for lethal outcomes, including asphyxiation and cardiac events.[6] This call is answered by Rep. Pierick's proposed bill, which aims to curb restraint use by implementing stronger safeguards and making these methods a last resort.
Studies such as the one about the Pennsylvania State Hospital System, which successfully eliminated the use of restraints and seclusion across multiple hospitals between 2011 and 2020, show that it is possible to improve patient safety while phasing out these harmful practices. The 2022 study of experience, published in Psychiatry Online, examined the effect of this change on key safety measures: physical restraint, assaults, aggression, and self-injurious behavior. It found key safety metrics improved, including a significant reduction in restraint duration and incidents of physical restraint.[7]
Global Momentum Against Restraint Practices
CCHR supports a nationwide movement to eliminate physical and chemical restraints, advocating for the passage of similar legislation in all states.
Globally, the call to end restraint practices is growing. In October 2023, the World Health Organization and the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights issued guidance emphasizing the severe harm caused by coercive psychiatric practices, including restraints.[8] These organizations join CCHR in advocating for an absolute ban on all coercive measures, including restraint and forced detention in mental hospitals.
More on The Californer
CCHR is committed to seeing Rep. Pierick's bill become law in Hawaii and to replicate similar legislative efforts across the U.S. to protect vulnerable patients.
The group, which was established in 1969 by the Church of Scientology and eminent professor of psychiatry Dr. Thomas Szasz, was one of the groups that were instrumental in obtaining federal regulatory reforms regarding restraints. However, CCHR International's President, Jan Eastgate, says a greater unified movement is still needed to prevent further deaths and trauma within the psychiatric system.
Sources:
[1] trackbill.com/bill/hawaii-house-bill-1394-restraint-seclusion-minors-vulnerable-adults-hospitals-medical-facilities/2638204/
[2] www.cchrint.org/2022/06/29/us-could-learn-from-reform-of-coercive-mental-health-practices/; "National Review of Restraint Related Deaths of Children and Adults with Disabilities: The Lethal Consequences of Restraint," Equip for Equality, 2011, www.equipforequality.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/National-Review-of-Restraint-Related-Deaths-of-Adults-and-Children-with-Disabilities-The-Lethal-Consequences-of-Restraint.pdf; "Race-Based Disparities in the Frequency and Duration of Restraint Use in a Psychiatric Inpatient Setting," Psychiatric Services, 1 Apr. 2024, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37855100/
[3] Colin M. Smith, et al., "Association of Black Race With Physical and Chemical Restraint Use Among Patients Undergoing Emergency Psychiatric Evaluation," Psychiatry Online, 21 Dec. 2021, psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202100474
[4] www.cchrint.org/2024/05/31/journal-urges-its-time-to-regulate-troubled-teen-behavioral-programs/
[5] Deborah Yetter, "7-year-old died at Kentucky youth treatment center due to suffocation, autopsy finds; 2 workers fired," Louisville Courier-Journal, 19 Sept. 2022, www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2022/09/19/death-child-jaceon-terry-brooklawn-kentucky-youth-center/10428004002/
[6] "Toward the Cessation of Seclusion and Mechanical Restraint Use in Psychiatric Hospitals: A Call for Regulatory Action," Psychiatric Services, Jan. 2024,
psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202100538
[7] Gregory M. Smith, "Effects of Ending the Use of Seclusion and Mechanical Restraint in the Pennsylvania State Hospital System, 2011–2020," Psychiatry Online, 20 July 2022, psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202200004
[8] "Mental health, human rights and legislation," World Health Organization and United Nations, www.who.int/publications/b/70051
CCHR underscores the importance of this legislation during Black History Month, spotlighting the alarming over-representation of racial minorities among those subjected to restraints and seclusion in the mental health system. The bill only permits the use of restraint in rare instances where there is an immediate risk of harm to the patient or others, and only after less intrusive measures have been attempted.
A 2011 report found that African Americans were disproportionately affected by restraint-related deaths, making up 22% of the studied deaths while only comprising 13% of the U.S. population. In addition, Black and multiracial patients are more likely to experience restraints, often for longer periods, than their white peers.[2] In 2021, a study of adults receiving an emergency psychiatric evaluation between January 1, 2014, and September 18, 2020, at a large academic medical center revealed Black patients continued to be at higher risk of experiencing physical or chemical restraint compared with White patients.[3]
Responding to high numbers of restraint deaths, in 2020, CCHR formed its Task Force Against Racism and Modern-Day Eugenics, led by Reverend Frederick Shaw, aimed at ending physical and chemical restraint deaths, particularly prevalent among minority communities.
More on The Californer
- Contracting Resources Group Receives 2025 HIRE Vets Platinum Medallion Award from the U.S. Department of Labor
- The Iconic Cops TV Show Is Now Streaming on AwepraTV
- Matt Ox Releases New Visual Content Highlighting Artistic Growth and Collaboration
- Silva Construction Unveils 2026 Design Trends
- California: Governor Newsom announces appointments 12.12.2025
This followed the death of a 16-year-old African American boy after being restrained in the now-closed residential behavioral facility for teens in Michigan. The Kalamazoo County Medical Examiner's office determined the death was a homicide and three staff were charged with involuntary manslaughter and second-degree child abuse—all pleading guilty.[4]
Two years later, another shocking tragedy was the death of a 7-year-old foster care child who was restrained and killed at a psychiatric residential center in Louisville, Kentucky on July 17, 2022. In September, the medical examiner also ruled that death a homicide.[5]
Their deaths underscored the urgent need for legislative action because, despite the clear risks, the practice of using seclusion and mechanical restraints remains common in psychiatric facilities. A 2023 report from Psychiatric Services issued a call for regulatory action to end these practices due to the significant trauma and potential for lethal outcomes, including asphyxiation and cardiac events.[6] This call is answered by Rep. Pierick's proposed bill, which aims to curb restraint use by implementing stronger safeguards and making these methods a last resort.
Studies such as the one about the Pennsylvania State Hospital System, which successfully eliminated the use of restraints and seclusion across multiple hospitals between 2011 and 2020, show that it is possible to improve patient safety while phasing out these harmful practices. The 2022 study of experience, published in Psychiatry Online, examined the effect of this change on key safety measures: physical restraint, assaults, aggression, and self-injurious behavior. It found key safety metrics improved, including a significant reduction in restraint duration and incidents of physical restraint.[7]
Global Momentum Against Restraint Practices
CCHR supports a nationwide movement to eliminate physical and chemical restraints, advocating for the passage of similar legislation in all states.
Globally, the call to end restraint practices is growing. In October 2023, the World Health Organization and the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights issued guidance emphasizing the severe harm caused by coercive psychiatric practices, including restraints.[8] These organizations join CCHR in advocating for an absolute ban on all coercive measures, including restraint and forced detention in mental hospitals.
More on The Californer
- Interpreters Unlimited Helps NORAD Track Santa in More Languages Than Ever Before
- Quantum Capital Partners Secures $26M Construction Financing to Kickstart Major Mixed-Use Activation
- City of Long Beach Announces Awardees for Love Your Block Mini-Grant Program
- Updated EasyDesktop 10 organizer is the answer to time-wasting icon overload
- Long Beach Parks, Recreation and Marine Older Adult Program Returns to Expo Arts Center
CCHR is committed to seeing Rep. Pierick's bill become law in Hawaii and to replicate similar legislative efforts across the U.S. to protect vulnerable patients.
The group, which was established in 1969 by the Church of Scientology and eminent professor of psychiatry Dr. Thomas Szasz, was one of the groups that were instrumental in obtaining federal regulatory reforms regarding restraints. However, CCHR International's President, Jan Eastgate, says a greater unified movement is still needed to prevent further deaths and trauma within the psychiatric system.
Sources:
[1] trackbill.com/bill/hawaii-house-bill-1394-restraint-seclusion-minors-vulnerable-adults-hospitals-medical-facilities/2638204/
[2] www.cchrint.org/2022/06/29/us-could-learn-from-reform-of-coercive-mental-health-practices/; "National Review of Restraint Related Deaths of Children and Adults with Disabilities: The Lethal Consequences of Restraint," Equip for Equality, 2011, www.equipforequality.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/National-Review-of-Restraint-Related-Deaths-of-Adults-and-Children-with-Disabilities-The-Lethal-Consequences-of-Restraint.pdf; "Race-Based Disparities in the Frequency and Duration of Restraint Use in a Psychiatric Inpatient Setting," Psychiatric Services, 1 Apr. 2024, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37855100/
[3] Colin M. Smith, et al., "Association of Black Race With Physical and Chemical Restraint Use Among Patients Undergoing Emergency Psychiatric Evaluation," Psychiatry Online, 21 Dec. 2021, psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202100474
[4] www.cchrint.org/2024/05/31/journal-urges-its-time-to-regulate-troubled-teen-behavioral-programs/
[5] Deborah Yetter, "7-year-old died at Kentucky youth treatment center due to suffocation, autopsy finds; 2 workers fired," Louisville Courier-Journal, 19 Sept. 2022, www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2022/09/19/death-child-jaceon-terry-brooklawn-kentucky-youth-center/10428004002/
[6] "Toward the Cessation of Seclusion and Mechanical Restraint Use in Psychiatric Hospitals: A Call for Regulatory Action," Psychiatric Services, Jan. 2024,
psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202100538
[7] Gregory M. Smith, "Effects of Ending the Use of Seclusion and Mechanical Restraint in the Pennsylvania State Hospital System, 2011–2020," Psychiatry Online, 20 July 2022, psychiatryonline.org/doi/10.1176/appi.ps.202200004
[8] "Mental health, human rights and legislation," World Health Organization and United Nations, www.who.int/publications/b/70051
Source: Citizens Commission on Human Rights
Filed Under: Consumer, Medical, Health, Government, Science, Citizens Commission On Human Rights, CCHR International
0 Comments
Latest on The Californer
- EnergyStrat Launches Global LNG Risk Outlook 2025–2030
- bisco industries New Authorized Line: SKF Aerospace
- Strong Revenue Gains, Accelerating Growth, Strategic Hospital Expansion & Uplisting Advancements: Cardiff Lexington Corporation (Stock Symbol: CDIX)
- Baby Boomers: The Perfect Cash Buyers in Today's Market
- Stray Theories Unveils Falter, an Atmospheric Passage Through the Spaces Between Doubt and Hope
- Holiday Decorations Most Likely to Cause Injuries
- Daniel S. Romero, CFP® Earns Renowned Certification for Fiduciary Excellence
- UK Financial Ltd Confirms Official Corporate Structure of the Maya Preferred Project and Its Dual-Class Token System
- California: Coho salmon are making a comeback in the Russian River for the first time in 30 years
- DKN Hotels Acquires Residence Inn by Marriott San Diego Sorrento Mesa/Sorrento Valley
- CCHR Florida Joins Global Call to Ban Electroshock Treatment, Citing New Evidence of Widespread Patient Harm
- BoxingRx Announces Full Gym Renovation Ahead of New Ownership's One-Year Anniversary
- UK Financial Ltd Announces It's Official Corporate Headquarters In The United Kingdom
- Rigani Press Announces Breakthrough Book for Health IT and Medical Leaders to Forge the Road to Responsible AI
- FreeTo.Chat - The bold, Anonymous Confession Platform, ushers in a new era of tension relief
- Touchless Car Wash in Northridge CA
- California: Governor Newsom, First Partner join LA fire survivors Jude and Rebecca Kessler for 94th annual Capitol Tree lighting ceremony
- YouTube Tag Generator Launches Free SEO Tool to Boost Video Visibility
- In partnership with Berenson Cancer Center, mQOL presents feasibility study results at ASH meeting
- TKP Studios Announces Development of New True-Crime Television Series "Dorothy"